The Anatomy of a Phishing Attack
Understanding the Tactics Behind Phishing Attacks and How to Defend Your Business
Phishing attacks are one of the most common and costly cyber threats to businesses around the world. Even though more people are aware of them, these scams still work because they keep changing their tactics and use psychological tricks. The first step in protecting your business is to understand how these attacks happen.
In this blog, we will explain what a phishing attack is, look at the tricks hackers use to fool employees, and provide practical tips to help prevent these cyber threats.
What Is a Phishing Attack?
A phishing attack is a cybercrime where hackers trick people into giving away sensitive information, like login details or credit card numbers. These attacks often appear as emails, text messages, or phone calls that seem legitimate.
Don’t get caught by phishing scams!
Let’s set up defenses that actually work.
Why Are Phishing Attacks So Effective?
Phishing attacks take advantage of human emotions and technical weaknesses. Hackers often use feelings like fear, urgency, curiosity, or trust to trick their targets. For example, an email that looks like it’s from your bank may warn about a suspicious transaction. This can quickly create alarm, leading you to act without thinking twice.
Breaking Down the Anatomy of a Phishing Attack
Phishing attacks follow a clear process. Here’s how hackers plan and carry out these scams:
Research and Target Selection
Phishing attacks begin when hackers choose their targets. They may focus on a specific person, a department, or the whole organization, depending on their goal. To prepare, they often gather information that is publicly available from social media, company websites, or past data breaches.
Tactic Example:
- A hacker can use LinkedIn to find an employee in the finance department and create targeted phishing attacks that are specific to their job.
Crafting the Bait
After selecting a target, hackers create their “bait.” This bait is part of the phishing scheme designed to trick the victim into taking action. They often make emails or websites that look real and trustworthy. They carefully copy logos, fonts, and language to appear as a trusted organization.
Common Tactics:
- Spoofed Email Addresses: An email address like [email protected] might trick someone into thinking it’s from their bank.
- Look-Alike URLs: Hackers may use URLs like www.amaz0n-secure.com instead of www.amazon.com.
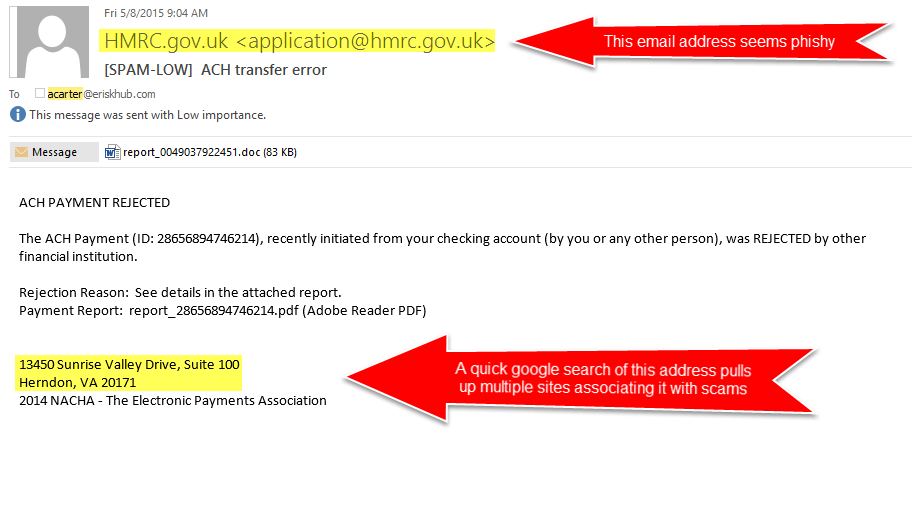
The Hook: Emotional Manipulation
Phishing attacks often succeed because they play on our emotions. Hackers use psychological tricks to create feelings of urgency, fear, or excitement. This pressures employees to act quickly without checking if the message is real.
Examples of Emotional Hooks:
- Urgency: “Your account will be locked unless you verify your information now!”
- Fear: “Suspicious login detected. Secure your account immediately.”
- Curiosity: “Congratulations! You’ve won a $1,000 gift card. Click here to claim it.”
Stop Stressing Over IT – Let Us Handle Your Support!
Focus on growing your business while we take care of your IT Support needs.
The Trap: Call-to-Action
Phishing emails or messages often try to trick you into doing something. They usually ask you to:
- Click on a harmful link.
- Download a dangerous attachment.
- Share sensitive information through a fake form.
Red Flags to Watch For:
- Hyperlinks that don’t match the official URL.
- Unexpected attachments from unknown senders.
- Requests for sensitive information via email or text.
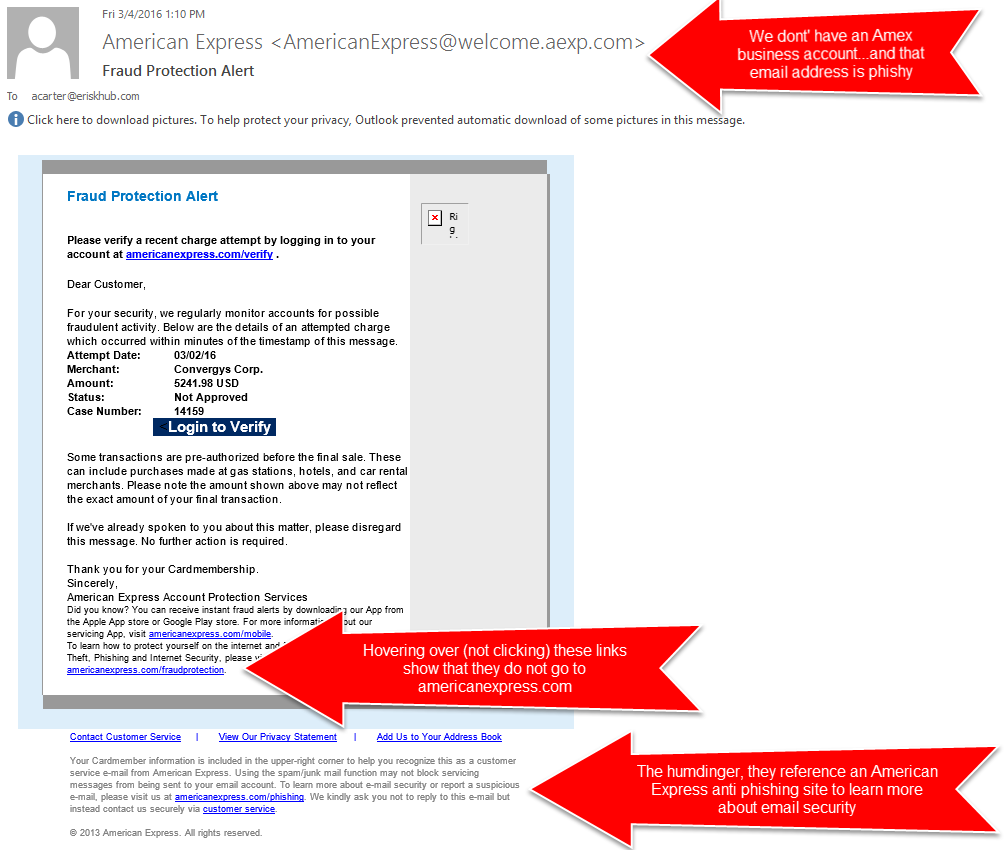
Execution and Data Harvesting
When the victim responds to the hacker’s call to action, the hacker gains access to sensitive information or installs harmful software on the victim’s device. This can lead to stolen credentials, unauthorized access to company systems, or even theft of money.
Potential Outcomes:
- Credential Harvesting: Login information is stolen and used for further attacks.
- Financial Loss: Funds are transferred directly to the hacker’s account.
- Ransomware Deployment: Clicking the link may install ransomware, locking critical systems until a ransom is paid.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks come in different forms. Hackers use various techniques to increase their chances of success.:
Email Phishing
The most common form of phishing involves fraudulent emails that appear to be from trusted sources.
Example: An email from “IT Support” asking employees to reset their password using a provided link.
Spear Phishing
This type of phishing targets specific people or organizations. The emails are personalized, which makes them harder to recognize as scams.
Example: A fake email from the CEO requesting a wire transfer to a vendor.
Whaling
Whaling is a scam that targets high-level executives. These attacks use fake invoices, legal threats, or requests for sensitive company information to trick people.
Example: A fake subpoena emailed to the CFO, demanding immediate action.
Smishing
Phishing through text messages, also called SMS phishing, is becoming more common as more people use mobile devices.
Example: A text claiming your bank account is locked, with a link to “verify” your information.
Vishing
Vishing, or voice phishing, is when hackers call people and pretend to be from trusted organizations. Their goal is to get sensitive information from you.
Example: A caller claiming to be from the IRS demanding immediate payment of taxes.
How to Protect Your Business from Phishing Attacks
To prevent phishing attacks, use technology, provide training, and stay alert. Here are some ways to protect your business:
1. Implement Advanced Email Security
Use email security solutions to find and block phishing emails before they get to employees. Tools like spam filters and AI-based email checks can greatly reduce phishing attempts.
2. Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Teach employees about phishing tricks and how to spot suspicious emails or messages. Run phishing tests to help them improve their skills in recognizing these threats.
3. Verify Requests Through Secondary Channels
Ask employees to confirm requests for sensitive information or financial transactions by contacting the requester through a phone call.
4. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
If login details are stolen, multi-factor authentication (MFA) helps keep your accounts safe by asking for a second proof of identity.
5. Keep Systems and Software Updated
Keep your systems and software updated regularly. This helps fix weaknesses that hackers might use in phishing attacks.
Still putting out IT fires? Let us prevent them.
It’s time to get ahead of the game and stop reacting to tech issues.
Phishing attacks are a constant threat to your organization. However, you can reduce this risk with awareness, training, and the right technology. When employees understand how phishing attacks work and recognize common tricks, they can help protect against cyber threats.
Invest in cybersecurity awareness training, use strong security tools, and create a culture of vigilance. These steps can help keep your business secure and stay ahead of hackers.
Get Started with Managed IT Services Today!
